The drive shaft is a crucial component in any vehicle, whether it’s small or large, as it plays an important role in ensuring your car runs smoothly and fluidly. This essential mechanism is part of the drivetrain system, which is responsible for transferring torque from the engine to the wheels, enabling the vehicle to move. Hidden from view, the drive shaft works tirelessly to connect various components, such as the transmission and differential, and maintain optimal performance even under stress. For automotive enthusiasts and professionals, understanding the drive shaft is key to recognizing its benefits, addressing common issues, and ensuring its longevity through proper maintenance.
Without a well-functioning drive shaft, the drivetrain system can fail, leading to significant damage or breakdowns. The drive shaft ensures that power is transferred efficiently between the engine and driven components, which makes it an important part of the vehicle’s machinery. Its durability and performance rely on timely replacements, as well as regular care to handle the stress caused by everyday driving. By focusing on the basics of this interesting component, you can better understand how the drive shaft contributes to a seamless and exciting driving experience.
Understanding the Drive Shaft
A driveshaft is a vital mechanical component found in many vehicles, especially those with rear-wheel drive, four-wheel drive, or all-wheel drive systems. It is responsible for transmitting rotational power from the engine to the wheels, enabling the vehicle to move. This cylindrical metal rod or tube connects different parts of the drivetrain, such as the differential and transmission, ensuring the power reaches the wheels. Without a properly functioning driveshaft, the vehicle won’t be able to move smoothly or efficiently.
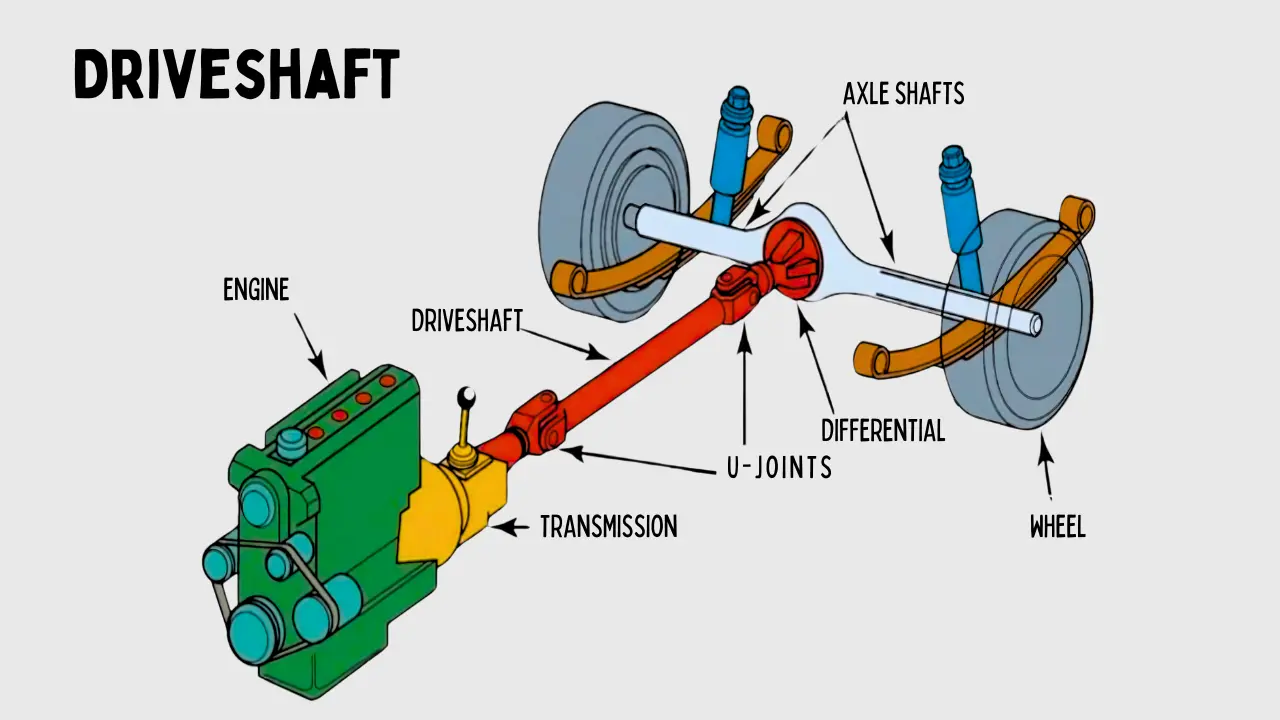
The driveshaft uses several key components like U-joints, slip yokes, and a center support bearing to allow for the necessary movement. These parts work together to help rotate the wheels at different speeds, a function particularly important in vehicles that handle varying driving conditions. The driveshaft works in tandem with the differential and transmission, transmitting the power needed for motion and enabling the wheels to rotate smoothly.
The driveshaft is a hidden yet essential component in a vehicle, and its role in transferring power from the engine to the wheels is critical. It’s a simple but significant part of the mechanism that keeps the vehicle running smoothly, making it an essential part of the vehicle’s drivetrain.
Purpose of a Driveshaft
- Drive Shaft (Propeller Shaft or Cardan Shaft
- Transferring Torque from Engine to Wheels
- Connecting Key Drive-train Components
- Materials Used in Drive Shaft Construction
- Drive Shaft Function in Various Vehicle Types
- Ensuring Efficient Movement Over Different Distances and Conditions
Key Components of a Driveshaft
- Several key components work together to transfer torque from the engine to the wheels.
Main Body of the Driveshaft
- Typically made from steel or aluminum.
- Provides necessary rigidity and structural strength.
Universal Joints or U-Joints
- Connect the tubing at both ends.
- Allow for angular movement and provide flexibility to compensate for drivetrain geometry.
Drive Shaft Sections and Articulation
- Joints help connect different driveshaft sections.
- Allow articulation and handle suspension movement.
Slip Yoke
- Adjusts the length of the driveshaft to accommodate suspension movement.
Center Support Bearing
- Supports longer driveshafts and reduces vibrations.
Flanges and Yokes
- Used to connect the transmission, differential, and wheels.
- Create a solid mechanical connection.
Power Transfer and Vehicle Movement
- These components work together to ensure the driveshaft transfers power to the wheels, allowing the vehicle to move smoothly and efficiently.
Driveshafts and Vehicle Operation
- Transferring torque from the transmission to the drive wheels
- Maintaining a strong connection between drive-train components
Type of Driveshaft Based on Design and Suspension Movement
- Dependent on vehicle design and suspension
One-Piece Solid Shaft
- Common in vehicles with shorter wheelbases, like passenger cars or light-duty trucks
- Made from a single solid metal piece
- Directly connects transmission, differential, and axle
Two-Piece Shaft
- Used in vehicles with longer wheelbases
- Features two shorter shafts connected by a center support bearing
- Reduces vibration and allows for smoother operation
Slip-Yoke Drive Shafts
- Tailored for rear-wheel-drive and all-wheel-drive vehicles
- Accommodates axle movement in systems like leaf-spring suspensions
- Adjusts shaft length as the drivetrain flexes
How a Driveshaft Works ?
The driveshaft is a key part of a vehicle that transmits power from the engine to the wheels. When the engine generates power, this force travels through the transmission and reaches the driveshaft, which rotates and transfers the torque to the differential. The differential then engages the wheels, allowing the vehicle to move. The driveshaft works in tandem with other components like the transmission and differential to deliver power to the wheels efficiently.
The driveshaft is essentially a spinning tube that transmits the rotational force generated by the engine. This force is passed along through the transmission and differential, and then to the rear axle or wheels, depending on the vehicle’s configuration. Universal joints in the driveshaft allow for flexibility, helping to accommodate changes in the drivetrain angles as the vehicle moves over bumps or turns. These joints help the driveshaft to absorb the movements and keep the power transfer smooth, without breaking the connection between the various parts.
As the vehicle moves, the driveshaft continuously rotates, transmitting power to the wheels, making sure the torque reaches the wheels and enables movement. Universal joints ensure that the driveshaft can flex and adjust to changes in the suspension or drivetrain angles, ensuring a smooth power transfer. This whole process is essential for the vehicle to move efficiently, with the driveshaft playing a vital role in linking the engine and wheels together.
Common Issues With Drive Shafts
The driveshaft is an essential part of your vehicle’s drivetrain, transmitting torque from the engine to the wheels. However, like any mechanical part, it can face several issues that may affect the vehicle’s handling and overall performance. Excessive vibrations, noise, and imbalance are common signs that something is wrong. These issues are often caused by worn universal joints (U-joints) or misalignment, which can disrupt the smooth transfer of power from the transmission to the wheels. If not addressed promptly, these problems can lead to serious damage to the driveshaft and other drivetrain components.
Some of the most noticeable symptoms of driveshaft issues include strange sounds, such as clunking noises, vibrations, and unusual handling while driving. These sounds often indicate worn U-joints or misalignment in the drivetrain. If you notice these signs, it’s important to check the driveshaft for any worn parts, like U-joints or center bearings. A mechanic can inspect the driveshaft and diagnose the problem, potentially identifying issues like worn bushings, rust, or loose components that need to be replaced. Lubrication and proper installation techniques can help minimize wear and prevent premature failure.
Failing to address these issues can lead to more serious drivetrain failures. Misalignment and stress on the driveshaft can cause uneven weight distribution, which may worsen over time. Regular inspections and ensuring the driveshaft is properly lubricated will help maintain its function and prevent vibrations, handling problems, and wear. If you notice vibrations or hear strange noises underneath your vehicle, it’s important to take action immediately to prevent further damage.
Maintaining and Replacing Driveshafts
Proper maintenance and timely replacement of the driveshaft are essential for keeping your vehicle safe and running smoothly. Vibrations, rattling, and turning difficulties often signal damaged parts like U-joints or bearings that need attention. Ignoring these symptoms can lead to drivetrain failure, making the vehicle undrivable and posing a safety risk. Regular car maintenance and check-ups by a mechanic can help identify issues early, ensuring the safe and smooth operation of your vehicle.
When the driveshaft is visibly damaged, immediate replacement is crucial. The process involves removing the old shaft, carefully disconnecting it from the transmission and differential, and installing a replacement part that fits the exact parameters. Ensuring the new driveshaft is properly aligned and securely fastened is vital to avoid further failure. Tools like wrenches, screwdrivers, and lubricants are used during the procedure, and a professional mechanic should handle the job for optimal results.
Routine inspections of the driveshaft and surrounding components can prevent deterioration and costly repairs. Watch for strange noises, intense vibrations, or difficulty during acceleration, as these are signs of wear. By addressing these problems promptly, you reduce the risk of damage to the entire drivetrain and ensure your vehicle remains safe to driv
FAQs
What are signs of a bad drive shaft?
A bad driveshaft can cause vibrations and strange noises while driving. If the driveshaft isn’t properly lubricated, dirt and grime can damage its moving parts, leading to faster wear. Regularly using high-temperature grease on critical parts and performing frequent oil changes as recommended can help extend the life of your vehicle and prevent these issues.
How much does it cost to replace a driveshaft?
The cost to replace a driveshaft typically ranges from $500 to $1000, with labor costing around $200 and parts making up the other half. For more complex repairs, the total can reach $1500 to $1700, depending on the process and the Drive Shaft Repair service invested in.
How easy is it to fix a drive shaft?
Repairing a drive shaft can be complicated and time-consuming, making it best to have a professional inspect it for signs of wear or damage. They can determine the necessary repairs and the best course of action to restore functionality.
How many hours does it take to replace a drive shaft?
Replacing a drive shaft typically takes 1 to 3 hours, depending on the vehicle and the complexity of the job.
What is the life of a drive shaft?
The lifespan of a rear drive shaft can vary based on factors like the make and model of the car, driving conditions, and the maintenance schedule, lasting longer if properly maintained.
